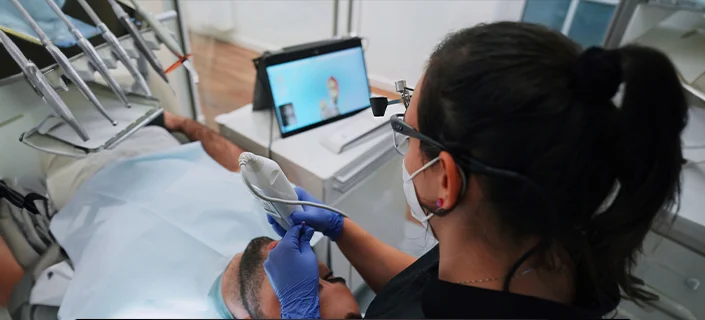
Digital impressions represent a significant improvement over traditional impression methods and offer numerous advantages that are important for both the practitioner and the patient:
• Real-time display: One of the outstanding features of digital impressions is their real-time display. This allows the dentist to make immediate checks and adjustments. If a problem arises during the scanning process or an area has not been adequately captured, the practitioner can react immediately and make corrections without the patient needing a new appointment.
• Repeatability and selectivity: Digital impression systems offer high repeatability and selectivity. This means that specific areas in the mouth can be targeted, which is particularly advantageous for complex restorations or in orthodontics. In addition, digital technology allows the same region to be captured repeatedly to ensure the best quality and accuracy.
• No model wear: Unlike physical impressions, which can wear out over time, digital models are permanent and can be modified or reprinted without loss of quality. This is particularly important for long-term archiving of patient data and for cases where future comparisons or re-treatments are required.
• Hygiene: Digital impressions are more hygienic than conventional methods. As no physical impression materials are used, there is no need for disinfection and cleaning. This reduces the risk of cross-contamination and improves general practice hygiene.
• Analysis options: Digital models allow for detailed examination and analysis. With advanced software, dentists can thoroughly analyze various aspects of tooth structure and occlusion, leading to more accurate diagnosis and treatment planning.
• Material savings: Digital impressions eliminate the cost and effort of traditional impression materials such as alginate or silicone. This not only leads to cost savings, but is also more environmentally friendly as fewer disposable materials are used.
• Direct further processing: Digital impression data can be seamlessly integrated into the digital workflow. This speeds up the process of manufacturing dentures, orthodontic appliances or surgical guides and enables more efficient collaboration with dental laboratories.
• Chairside procedure: Digital impressions allow dentists to use chairside procedures, which means that dentures or orthodontic appliances can be produced directly in the practice. This significantly reduces the waiting time for patients and enables faster treatment.
Overall, digital impressions offer a combination of precision, efficiency and patient comfort that makes them an indispensable technology in modern dentistry.